Electrically Conductive Silicone
Electrically conductive solid silicone sheet from ElastaPro is fabricated into gaskets and used in electrical cabinets and printed circuit boards (PCBs). These solid silicone sheet materials are also fabricated into elastomeric shielding gaskets that provide resistance against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).
Conductive silicones are compounds that combine the advantages of silicone rubber with the electrical properties of metals. Silicone offers thermal stability over a wide temperature range and resist water, ozone, and ultraviolet (UV) light. When filled with tiny metal particles, silicones combine environmental sealing with EMI shielding.
65 Durometer Electrically Conductive Silicone
Conductive solid silicone sheeting from ElastaPro comes in the following durometer.
This solid silicone sheeting is easily die cut and provides a superior gasket and sealing solution. Thicknesses range from .020” to .375”. This product is black in color
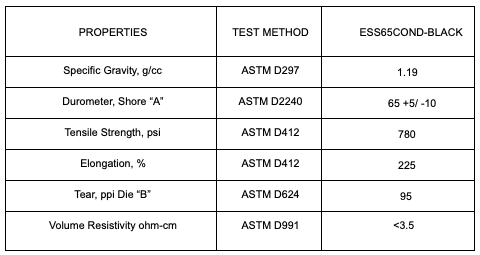
Material Properties
Some conductive silicone sheets use metal or metal-coated particles as the rubber filler material. The dielectric strength of silicone rubber depends on the specimen. High voltage silicone rubber is a highly specialized material and not typical of conductive silicone rubber sheet.
This table shows properties and test methods for specific products.
Additional Information
Electrically conductive silicone is a specialized type of silicone rubber formulated with conductive fillers—such as carbon, silver, nickel, or graphite—to provide electrical conductivity while retaining the flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance of standard silicone. This material is designed to conduct electricity or shield electronic components from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI), making it essential for applications in electronics, telecommunications, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Conductive silicone maintains the core advantages of traditional silicone, including wide temperature stability (typically from -55°C to +200°C), resistance to moisture, UV radiation, ozone, and many chemicals, and long-term aging performance. By incorporating conductive fillers, it gains the ability to dissipate static charges, ground electrical currents, and block EMI/RFI emissions.
One common use is in EMI shielding gaskets, where conductive silicone is used to seal enclosures and prevent electromagnetic interference from leaking in or out. It is also used in keypad contacts, connector gaskets, and grounding pads. The material is often manufactured as sheets, extrusions, molded parts, or coated fabrics, and can be tailored for specific electrical resistivity requirements—ranging from low-resistance grades for grounding to higher-resistance versions for static dissipation.
Electrically conductive silicone is especially valuable in environments where both environmental sealing and electrical conductivity are required, such as in military and aerospace enclosures governed by MIL-DTL-83528 standards. It is also used in cleanrooms and medical electronics where non-corrosive, biocompatible conductive materials are needed.
Overall, electrically conductive silicone combines the protective and flexible properties of silicone rubber with the functionality of metal-based conductivity. This makes it a go-to solution for engineers designing sensitive electronic systems that must operate reliably in electrically noisy or environmentally demanding conditions.

